Duplication d’un environnement
Il peut être nécessaire de dupliquer un environnement par exemple pour mettre en production un environnement de test qui a passé avec succès la validation. Voici les étapes à suivre :
- Dupliquer les serveurs
- Renommer les DNS
Duplication des serveurs
L’hébergement est de plus en plus souvent réalisé sur des machines virtuelles. La duplication des serveurs devient une opération simple.
- Arrêter les services (Apache, Tomcat, Solr puis MySQL) sur le serveur source
- Dupliquer l’ensemble des machines
Renommer les DNS
Le renommage des DNS est détaillé dans la section ci-dessous : Modifier l’URL du Back-office
Tests
- Se connecter au nouveau CMS
- Créer une page, un nouveau contenu et valider le contenu, rendre cette page accessible (étiqueter si besoin)
- Faire une recherche de contenus dans le CMS et vérifier qu'elle n'échoue pas
- Se connecter à l’ancien CMS, vérifier que la page n’est pas sur l’ancien CMS
- Se connecter au nouveau site
- Accéder à la nouvelle page
- Se connecter à l’ancien site et vérifier que la nouvelle page n’existe pas sur l’ancien site
Duplication des données
La duplication des données peut être utile pour copier les données de production sur un environnement de test.
Les données gérées par le CMS sont stockées dans une base JCR. Plusieurs implémentations sont possibles :
- Système de fichiers
- Base de données (avec complément en système de fichiers)
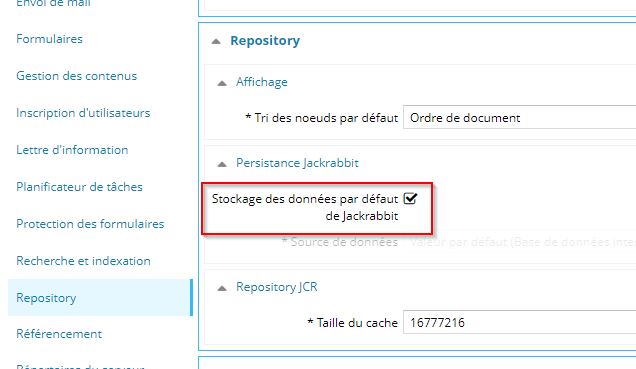
Pour connaître la façon dont sont stockées vos données, il faut se rendre dans l'administration du CMS http://cms.xxxxxx.fr/_admin (utiliser les identifiants de l’administration, par défaut : admin/admin), dans la section Repository :
Si la case à cocher « Stockage des données par défaut de Jackrabbit » est cochée, alors votre implémentation est sur système de fichiers uniquement.
Dans le cas où cette case n'est pas cochée, la plupart des données sont stockées dans la base de données indiquée dans le champs Persistance Jackrabbit / Source de données.
L'emplacement de vos données fichiers est défini dans la variable d'environnement AMETYS_CMS_HOME.
Les données stockées dans les bases de données sont définies dans votre configuration, à chaque fois que vous rencontrez une source de données.
Sur le serveur source
- Si possible arrêter Tomcat
- Suivre les étapes de sauvegarde : 4. Exploitation
- Redémarrer Tomcat
Sur le serveur cible
Récupérer l'archive du serveur source
Suivre les étapes de restauration : 4. Exploitation
Faire également une sauvegarde sur le serveur cible.
Ne relancez pas Tomcat à la fin de la restauration.Récupérer le dossier config des anciennes données et le remplacer dans $AMETYS_CMS_HOME/config
Faire de même avec le répertoire $AMETYS_CMS_HOME/data/internal-db
- Relancer Tomcat
Configuration
Lors de la récupération des données, nous n'avons pas récupéré le dossier config contenant l'ensemble de la configuration de l'application. Il vous sera peut être tout ou partiellement nécessaire.
Voici les différents fichiers que l'on peut retrouver dans ce dossier :
- config.xml : Ensemble des informations renseignées dans la configuration de l'administration (la plupart du temps, la configuration diffère d'un environnement de TEST à un environnement de PROD (URL, sources de données, mode, serveur mail, etc.).
- datasources-ldap.xml : Description des sources de données LDAP (Il arrive souvent que les sources LDAP soit très similaire entre le TEST et la PROD).
- datasources-sql.xml : Description des sources de données SQL (L'utilisation des mêmes bases de données en TEST et en PROD est rare sauf pour des besoins spécifiques en lecture seule).
- group-directories.xml : Description des répertoires de groupes.
- user-populations.xml : Description des populations d'utilisateurs (les populations sont souvent un peu différentes et plus restreintes dans un environnement de TEST).
- synchronizable-collections.xml : Description des collections synchronisables, il peut être utile de récupérer tout ou une partie des données de ce fichier afin de pouvoir continuer à synchroniser les données. Attention, les collections doivent porter le même identifiant en TEST et en PROD pour être compatibles.
Cette liste n'est pas exhaustive.
Espace disque
Afin d'éviter les problèmes d'espaces disque, n'oubliez pas de supprimer les données obsolètes.